- Giới thiệu
- Nhóm Công tác
- Tin tức
- Thông tin về FTA
- Tài Liệu
- Sự kiện
- Liên hệ
Solutions for sustainable growth of lobster farming
Tran Dinh Luan, director of the Directorate of Fisheries, proposed solutions for developing sustainable lobster farming in the South Central areas.
The provinces of the South Central are regarded as the "hub" of lobster cage farming, with Phu Yen and Khanh Hoa provinces constituting the dominance. In the past several years, lobster farming in the two provinces has become the most crucial aquaculture sector and the most important economic industry, contributing significantly to socioeconomic development, and providing steady income, and employment for most local workers
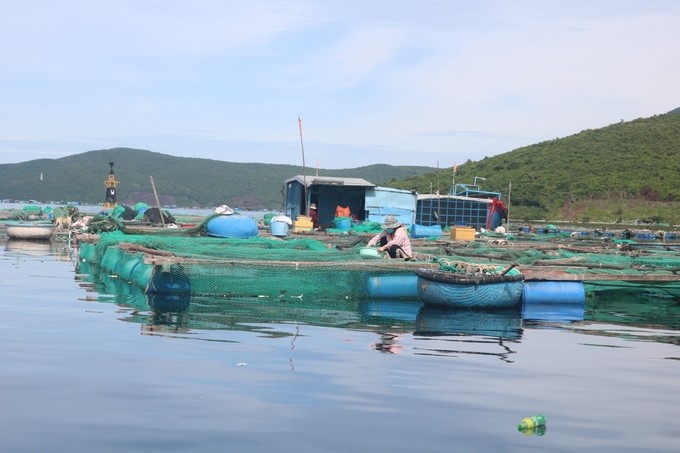

South Central is considered the capital of lobster farming
In Phu Yen province, lobster production reached 1,500 tons in 2021. According to the Phu Yen Department of Agriculture and Rural Development, the entire area stocked 96,114 lobster cages in 2022, including 64,985 cages in Song Cau town, 14,650 cages in Dong Hoa district, and 16,479 cages in Tuy An district.
According to the agricultural sector of Khanh Hoa province, the total number of lobster cages in the province is around 64,500, with an output of over 1,300 tons.
However, lobster farming in these provinces has encountered obstacles, including inappropriate seed management, feeds, and farming area administration. When it comes to natural catastrophes, diseases, a polluted environment, or lobsters for human consumption, which rely mostly on unofficial export channels, among others, lobster farming households are always exposed to hazards and difficulties.
In a conversation with Vietnam Agriculture News, the director of D-fish, Tran Dinh Luan, proposed several solutions for areas to promote lobster farming in a sustainable manner in light of these shortcomings and limitations.
Regarding production organization and management, localities should examine and control the plan to develop lobster production, including seed production area and consuming lobster farming area, in accordance with the content of the land use plan and seawater surface plan. In accordance with the Law on Fisheries 2017, certification of aquaculture and registration of cage farming are also needed.
Other solutions include reorganizing lobster farming in accordance with the value chain and constructing a model for a network of small production establishments comprised of cooperative groups, cooperatives, and professional associations affiliated with businesses supplying input materials and consuming products. Promoting the establishment of a Vietnamese lobster farming, processing, and exporting association. Inspect and monitor production operations, including the conditions of shrimp farming establishments, the manufacture and delivery of breeds, food, medicines, and chemicals, and environmental remediation goods and materials.
Concurrently, it is crucial to strengthen management over natural lobster exploitation by imposing rules on size, fishing lines, and season for natural lobster seeds. The use of new technology to develop a database on lobster production and export must be accelerated, as must the dissemination of information to educate the public about the need of preserving natural lobster seeds.
In the realms of science, technology, and extension, the Director General of the Directorate of Fisheries stated that it is vital to collaborate with nations such as Australia, New Zealand, and Japan to actively manufacture artificial spawn of cotton lobsters and blue lobsters. Focus on exploring and perfecting the technical method of onshore lobster farming with a circulating water filtration system and industrial feed at the same time.
Continue researching and refining the lobster farming method at several phases in order to enhance production, survival rate, feed utilization ratio, illness risk, and environmental effects. environment and increase farmers' economic efficiency. Utilizing innovative materials, investigate and evaluate a paradigm for lobster farming with high-tech applicability in offshore and open waters (such as HDPE cage frames).
He also advised researching and completing the technical process and production line of mixed feed on an industrial scale in order to decrease the feed utilization coefficient, cut expenses, raise resistance, and enhance the growth rate and ratio. Survival rate during raising; color improvement and environmental pollution control. In order to boost production, product quality, and sustainable development, training and transmission of technical developments, as well as replication of successful lobster farming methods in lobster farming facilities, were also highlighted.
Concerning disease prevention and adaptation to climate change, it is essential to do research and propose efficient disease preventive and control techniques for farmed lobsters, particularly for common illnesses. Strengthen the management of the environment and diseases in accordance with rules; design and implement automatic environmental monitoring and early alert systems in highly populated and crucial agricultural regions; provide timely alerts to address climate change.
It should enhance training and communication to increase lobster farmers' understanding and sense of responsibility for enforcing rules on disease control, farming techniques, natural disaster prevention, etc., as well as strengthen inspection and strictly deal with violations.
Local authorities establish and promulgate legislation governing the collection and treatment of trash in lobster farming regions; they also administer the management of garbage collection from lobster farming. For domestic consumption and export of lobster, it is recommended to construct a service system for transporting, conserving, and consuming live lobster items on the domestic market.
On the part of the State, promote trade promotion to increase the market for lobster goods in other countries, as well as coordinate discussions and eliminate impediments to the importation of lobster seed from countries such as Indonesia, the Philippines, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, and Singapore.
Attracting units to participate in creating and developing the distribution infrastructure for live lobsters, including sites of purchase and storage in regions of intense cultivation; transshipment points prior to distribution to manufacturing clean shrimp products, guarantee the quality, and traceability.
Continuing to apply technological solutions in processing and preservation, particularly investing in processing value-added products, preserving and transporting live lobsters in order to diversify products, improve the quality and competitiveness of Vietnamese lobster products, and increase their capacity
Tin liên quan
PSAV Attends the 30th Anniversary Celebration of Cargill Vietnam2025/10/23
Plant health management helps increase coffee yield up to 15%2025/10/16
An Giang to host 2025 OCOP forum for sustainable development2025/09/25
Viet Nam and France foster cooperation on blue economy and sustainable environment2025/09/29
Agriculture and Environment exhibition ready for National celebration2025/08/27



 Điều lệ hoạt động
Điều lệ hoạt động



















































